Why iPhone Third Party Chargers Are Better Than Original Apple Charger
2021-02-13
Why iPhone Third Party Chargers Are Better?
Apple at this year (2021) still using their charger technology from the mid 20's, as more and more third-party companies investing to a more better ways to deliver power to device which is more eco-friendly - this brings the Apple original chargers to be left alone in the dark.
The birth of GaN technology
Gallium nitride, or GaN, is a material that's starting to be used for semiconductors in chargers. It was used to make LEDs starting in the '90s, and it's also a popular material for solar cell arrays on satellites. The main thing about GaN when it comes to chargers is that it produces less heat.
What's a charger really do?
Before we look at GaN on the inside of a charger, let's take a look at what a charger does. Each of our smartphones, tablets, and laptops has a battery. When a battery is transferring power to our devices, what's happening is actually a chemical reaction. A charger takes an electrical current to reverse that chemical reaction. In the early days, chargers just sent juice to a battery constantly, which could lead to overcharging and damage. Modern chargers include monitoring systems that lower the current as a battery fills up, which minimizes the possibility of overcharging.
The heat is on: GaN replaces silicon
Since the '80s, silicon has been the go-to material for transistors. Silicon conducts electricity better than previously used materials—such as vacuum tubes—and keeps costs down, as it's not too expensive to produce. Over the decades, improvements to technology led to the high performance we're accustomed to today. Advancement can only go so far, and silicon transistors may be close to as good as they are going to get. The properties of silicon material itself as far as heat and electrical transfer mean the components can’t get any smaller.
GaN is different. It's a crystal-like material that's capable of conducting far higher voltages. Electrical current can pass through components made from GaN faster than silicon, which leads to even faster processing. GaN is more efficient, so there's less heat.
A transistor is essentially a switch. A chip is a component that has hundreds or even thousands of transistors in a very small space. What happens when GaN is used instead of silicon, is that everything can be closer together. That means more processing power can be packed into a smaller space. A small charger can do more work than a larger one, and can do it faster.
Why GaN is the future of charging
Most of us have a few electronic devices that need charging. With a charger that uses GaN technology, we get a whole lot more bang for our buck—both now and in the future.
Since the overall design is smaller, most GaN chargers incorporate USB-C Power Delivery. This offers fast charging for compatible devices. Most current smartphones allow fast charging of some kind and even more devices will have this option in the future.
The most efficient power
Being lightweight and occupying less space makes GaN chargers great for travel. One charger is all most people will need when it has enough power for everything from a phone to a tablet and even a laptop.
Heat is a major factor in determining how long electronic devices keep working, and chargers are no exception. The efficiency of GaN in transferring power keeps heat to a minimum, so a modern GaN charger will keep working for a lot longer than non-GaN chargers made even a year or two in the past.
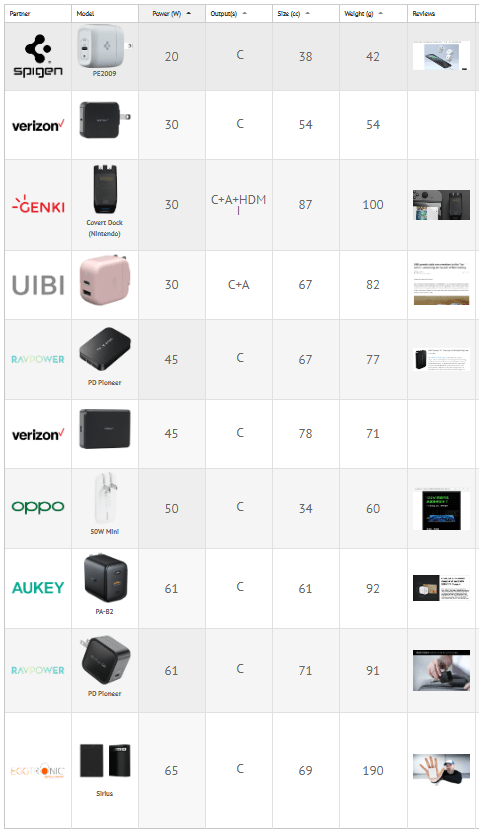
Below are the GaN chargers that you will need for your new iPhone 12 sorted by their power delivery.